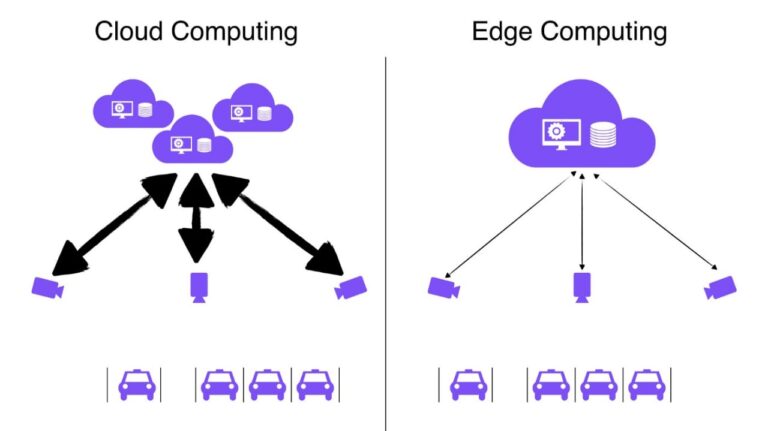
Computer vision is a branch of AI(Artificial Intelligence) that deals with visual data. The role of computer vision technology is to improve the way images and videos are interpreted by machines. It uses mathematics and analysis to extract important information from visual data.
There have been several innovations in computer vision technology in recent years. These innovations have significantly improved the speed and accuracy of AI.
Computer vision is a very important part of AI. Computer vision has many important AI applications like self-driving, facial recognition, medical imaging, etc. It also has many applications in different fields including security, entertainment, surveillance, and healthcare. Computer vision is enabling machines to become more intelligent with visual data.
All these innovations in computer vision make AI more human-like.
Computer Vision Technology#
In this article, we'll discuss recent innovations in computer vision technology that have improved AI. We will discuss advancements like object detection, pose estimation, semantic segmentation, and video analysis. We will also explore some applications and limitations of computer vision.
Image Recognition:#
Image recognition is a very important task in computer vision. It has many practical applications including object detection, facial recognition, image segmentation, etc.
In recent years there have been many innovations in image recognition that have led to improved AI. All the advancements in image recognition we see today have been possible due to deep learning, CNNs, Transfer technology, and GANs. We will explore each of these in detail.
Deep Learning#
Deep Learning is a branch of machine learning that has completely changed image recognition technology. It involves training models with a vast amount of complex data from images.
It uses mathematical models and algorithms to identify patterns from visual input. Deep learning has advanced image recognition technology so much that it can make informed decisions without a human host.
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs)#
Convolutional neural networks (CNNs) are another innovation in image recognition that has many useful applications. It consists of multiple layers that include a convolution layer, pool layer, and fully connected layer. The purpose of CNN is to identify, process, and classify visual data.
All of this is done through these three layers. The convolution layer identifies the input and extracts useful information. Then the pooling layer compresses it. Lastly, a fully connected layer classifies the information.
Transfer Learning#
Transfer learning means transferring knowledge of a pre-existing model. It is a technique used to save time and resources. In this technique instead of training an AI model with deep learning, a pre-existing model trained with vast amounts of data in the same field is used.
It gives many advantages like accurately saved costs and efficiency.
Generative Adversarial Network (GAN)#
GAN is another innovation in image recognition. It consists of two neural networks that are constantly in battle. One neural network produces data (images) and the other has to differentiate it as real or fake.
As the other network identifies images to be fake, the first network creates a more realistic image that is more difficult to identify. This cycle goes on and on improving results further.
Object Detection:#
Object detection is also a very crucial task in computer vision. It has many applications including self-driving vehicles, security, surveillance, and robotics. It involves detecting objects in visual data.
In recent years many innovations have been made in object detection. There are tons of object-detecting models. Each model offers a unique set of advantages.
Have a look at some of them.
Faster R-CNN#
Faster R-CNN (Region-based Convolutional Neural Network) is an object detection model that consists of two parts: Regional proposal network (RPN) and fast R-CNN. The role of RPN is to analyze data in images and videos to identify objects. It identifies the likelihood of an object being present in a certain area of the picture or video. It then sends a proposal to fast R-CNN which then provides the final result.
YOLO#
YOLO (You Only Look Once) is another popular and innovative object detection model. It has taken object detection to the next level by providing real-time accurate results. It is being used in Self-driving vehicles due to its speed. It uses a grid model for identifying objects. The whole area of the image/video is divided into grids. The AI model then analyzes each cell to predict objects.
Semantic Segmentation:#
Semantic segmentation is an important innovation in Computer vision. It is a technique in computer vision that involves labeling each pixel of an image/video to identify objects.
This technique is very useful in object detection and has many important applications. Some popular approaches to semantic segmentation are Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs), U-Net, and Mask R-CNN.
Fully Convolutional Networks (FCNs)#
Fully convolutional networks (FCNs) are a popular approach used in semantic segmentation. They consist of a neural network that can make pixel-wise predictions in images and videos.
FCN takes input data and extracts different features and information from that data. Then that image is compressed and every pixel is classified. This technique is very useful in semantic segmentation and has applications in robotics and self-driving vehicles. One downside of this technique is that it requires a lot of training.
U-Net#
U-Net is another popular approach to semantic segmentation. It is popular in the medical field. In this architecture, two parts of U- Net one contracting and the other expanding are used for semantic segmentation.
Contracting is used to extract information from images/videos taken through U shaped tube. These images/videos are then processed to classify pixels and detect objects in that image/video. This technique is particularly useful for tissue imaging.
Mask R-CNN#
Mask R-CNN is another popular approach to semantic segmentation. It is a more useful version of Faster R-CNN which we discussed earlier in the Object detection section. It has all the features of faster R-CNN except it can segment the image and classify each pixel. It can detect objects in an image and segment them at the same time.
Pose Estimation:#
Pose estimation is another part of computer vision. It is useful for detecting objects and people in an image with great accuracy and speed. It has applications in AR (Augmented Reality), Movement Capture, and Robotics. In recent years there have been many innovations in pose estimation.
Here are some of the innovative approaches in pose estimation in recent years.
Open Pose#
The open pose is a popular approach to pose estimation. It uses CNN(Convolutional Neural Networks) to detect a human body. It identifies 135 features of the human body to detect movement. It can detect limbs and facial features, and can accurately track body movements.
Mask R-CNN#
Mask R-CNN can also be used for pose estimation. As we have discussed earlier object detection and semantic segmentation. it can extract features and predict objects in an object. It can also be used to segment different human body parts.
Video Analysis:#

Video Analysis is another important innovation in computer vision. It involves interpreting and processing data from videos. Video analysis consists of many techniques that include. Some of these techniques are video captioning, motion detection, and tracking.
Motion Detection#
Motion detection is an important task in video analysis. It involves detecting and tracking objects in a video. Motion detecting algorithm subtracts the background from a frame to identify an object then each frame is compared for tracking movements.
Video Captioning#
It involves generating natural text in a video. It is useful for hearing-impaired people. It has many applications in the entertainment and sports industry. It usually involves combining visuals from video and text from language models to give captions.
Tracking#
Tracking is a feature in video analysis that involves following the movement of a target object. Tracking has a wide range of applications in the sports and entertainment industry. The target object can be a human or any sports gear. For example, some common target objects are the tennis ball, hard ball, football, and baseball. Tracking is done by comparing consecutive frames for details.
Applications of Innovations in Computer Vision#
Innovations in computer vision have created a wide range of applications in different fields. Some of the industries are healthcare, self-driving vehicles, and surveillance and security.
Healthcare#
Computer vision is being used in healthcare for the diagnosis and treatment of patients. It is being used to analyze CT scans, MRIs, and X-rays. Computer vision technology is being used to diagnose cancer, heart diseases, Alzheimer's, respiratory diseases, and many other hidden diseases. Computer vision is also being used for remote diagnoses and treatments. It has greatly improved efficiency in the medical field.
Self Driving Vehicles#
Innovation in Computer vision has enabled the automotive industry to improve its self-driving features significantly. Computer vision-based algorithms are used in car sensors to detect objects by vehicles. It has also enabled these vehicles to make real-time decisions based on information from sensors.
Security and Surveillance#
Another application of computer vision is security and surveillance. Computer vision is being used in cameras in public places for security. Facial recognition and object detection are being used for threat detection.
Challenges and Limitations#
No doubt innovation in computer vision has improved AI significantly. It has also raised some challenges and concerns about privacy, ethics, and Interoperability.
Data Privacy#
AI trains on vast amounts of visual data for improved decision-making. This training data is usually taken from surveillance cameras which raises huge privacy concerns. There are also concerns about the storage and collection of users' data because there is no way of knowing which information is being accessed about a person.
Ethics#
Ethics is also becoming a big concern as computer vision is integrated with AI. Pictures and videos of individuals are being used without their permission which goes against ethics. Moreover, it has been seen that some AI models discriminate against people of color. All these ethical concerns need to be addressed properly by taking necessary actions.
Interpretability#
Another important concern of computer vision is interpretability. As AI models continue to evolve, it becomes increasingly difficult to understand how they make decisions. It becomes difficult to interpret if decisions are made based on facts or biases. A new set of tools are required to address this issue.
Conclusion:#
Computer vision is an important field of AI. In recent years there have been many innovations in computer vision that have improved AI algorithms and models significantly. These innovations include image recognition, object detection, semantic segmentation, and video analysis. Due to all these innovations computer vision has become an important part of different fields.
Some of these fields are healthcare, robotics, self-driving vehicles, and security and surveillance. There are also some challenges and concerns which need to be addressed.





































































































-eaff56a6fbdde187cf68b7e5750b22c1.jpg)