Differentiation between Edge Computing and Cloud Computing | A Study
Are you familiar with the differences between edge computing and cloud computing? Is edge computing a type of branding for a cloud computing resource, or is it something new altogether? Let us find out!
The speed with which data is being added to the cloud is immense. This is because the growing number of devices in the cloud are centralized, so it must transact the information from where the cloud servers are, hence data needs to travel from one location to another so the speed of data travel is slow. If this transaction starts locally, then the data travels at a shorter distance, making it faster. Therefore, cloud suppliers have combined Internet of Things strategies and technology stacks with edge computing for the best usage and efficiency.
In the following article, we will understand the differences between cloud and edge computing. Let us see what this is and how this technology works.
EDGE COMPUTING#
Edge Computing is a varied approach to the cloud. It is the processing of real-time data close to the data source at the edge of any network. This means applications close to the data generated instead of processing all data in a centralized cloud or a data center. It increases efficiency and decreases cost. It brings the storage and power closer to the device where it is most needed. This distribution eliminates lag and saves a scope for various other operations.
It is a networking system, within which data servers and data processing are closer to the computing process so that the latency and bandwidth problems can be reduced.
Now that we know what the basics of edge computing are, let's dive in a little deeper for a better understanding of terms commonly associated with edge computing:
Latency#
Latency is the delay in contacting in real-time from a remotely located data center or cloud. If you are loading an image over the internet, the time to show up completely is called the latency time.
Bandwidth#
The frequency of the maximum amount of data sent over an Internet connection at a time is called Bandwidth. We refer to the speed of sent and received data over a network that is calculated in megabits per second or MBPS as bandwidth.
Leaving latency and bandwidth aside, we choose edge computing over cloud computing in hard-to-reach locations, where there is limited or no connectivity to a central unit or location. These remote locations need local computing, and edge computing provides the perfect solution for it.
Edge computing also benefits from specialized and altered device functions. While these devices are like personal computers, they are not regular computing devices and perform multiple functions benefiting the edge platform. These specialized computing devices are intelligent and respond to machines specifically.
Benefits of Edge Computing#
Gathering data, analyzing, and processing is done locally on host devices on the edge of the network, which has the caliber to be completed within a fraction of a second.
It brings analytical capabilities comparatively closer to the user devices and enhances the overall performance.
Edge computing is a cheaper alternative to the cloud as data transfer is a lengthy and expensive process. It also decreases the risk involved in transferring sensitive user information.
Increased use of edge computing methods has transformed the use of artificial intelligence in autonomous driving. Artificial Intelligence-powered and self-driving cars and other vehicles require massive data presets from their surroundings to function perfectly in time. If we use cloud computing in such a case, it would be a dangerous application because of the lag.
The majority of OTT platforms and streaming service providers like Netflix, Amazon Prime, Hulu, and Disney+ to name a few, create a heavy load on cloud network infrastructure. When popular content is cached closer to the end-users in storage facilities for easier and quicker access. These companies make use of the nearby storage units close to the end-user to deliver and stream content with no lag if one has a stable network connection.
The process of edge computing varies from cloud computing as the latter takes considerably more time. Sometimes it takes up to a couple of seconds to channel the information to the data centers, ultimately resulting in delays in crucial decision-making. The signal latency can translate to huge losses for any organization. So, organizations prefer edge computing to cloud computing which eliminates the latency issue and results in the tasks being completed in fractions of a second.
CLOUD COMPUTING#
A cloud is an information technology environment that abstracts, pools, and shares its resources across a network of devices. Cloud computing revolves around centralized servers stored in data centers in large numbers to fulfill the ever-increasing demand for cloud storage. Once user data is created on an end device, its data travels to the centralized server for further processing. It becomes tiresome for processes that require intensive computations repeatedly, as higher latency hinders the experience.
Benefits of Cloud Computing#
Cloud computing gives companies the option to start with small clouds and increase in size rapidly and efficiently as needed.
The more cloud-based resources a company has, the more reliable its data backup becomes, as the cloud infrastructure can be replicated in case of any mishap.
There is little to no service cost involved with cloud computing as the service providers conduct system maintenance on their own from time to time.
Cloud enables companies to help cut expenses in operational activities and enables mobile accessibility and user engagement framework to a higher degree.
Many mainstream technology companies have benefited from cloud computing as a resourceful platform. Slack, an American cloud-based software as a service, has hugely benefited from adopting cloud servers for its application of business-to-business and business-to-consumer commerce solutions.
Another largely known technology giant, Microsoft has its subscription-based product line ‘Microsoft 365' which is centrally based on cloud servers that provide easy access to its office suite.
Dropbox, infrastructure as a service provider, provides a service- cloud-based storage and sharing system that runs solely on cloud-based servers, combined with an online-only application.
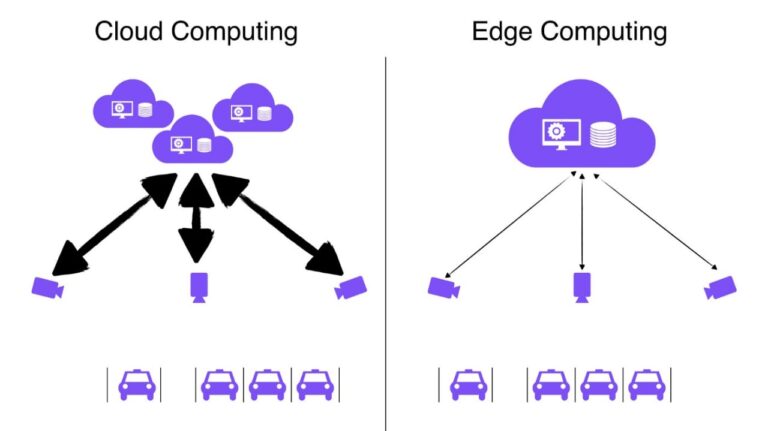
KEY DIFFERENCES#
The main difference between edge computing and cloud computing is in data processing within the case of cloud computing, data travel is long, which causes data processing to be slower but in contrast edge computing reduces the time difference in the data processing. It's essential to have a thorough understanding of the working of cloud and edge computing.
Edge computing is based on processing sensitive information and data, while cloud computing processes data that is not time constrained and uses a lesser storage value. To carry out this type of hybrid solution that involves both edge and cloud computing, identifying one's needs and comparing them against monetary values must be the first step in assessing what works best for you. These computing methods vary completely and comprise technological advances unique to each type and cannot replace each other.
The centralized locations for edge computing need local storage, like a mini data center. Whereas, in the case of cloud computing, the data can be stored in one location. Even when used as part of manufacturing, processing, or shipping operations, it is hard to co-exist without IoT. This is because everyday physical objects that collect and transfer data or dictate actions like controlling switches, locks, motors, or robots are the sources and destinations that edge devices process and activate without depending upon a centralized cloud.
With the Internet of Things gaining popularity and pace, more processing power and data resources are being generated on computer networks. Such data generated by IoT platforms is transferred to the network server, which is set up in a centralized location.
The big data applications that benefit from aggregating data from everywhere and running it through analytics and machine learning to prove to be economically efficient, and hyper-scale data centers will stay in the cloud. We chose edge computing over cloud computing in hard-to-reach locations, where there is limited connectivity to a cloud-based centralized location setup.
CONCLUSION#
The edge computing and cloud computing issue does not conclude that deducing one is better than the other. Edge computing fills the gaps and provides solutions that cloud computing does not have the technological advancements to conduct. When there is a need to retrieve chunks of data and resource-consuming applications need a real-time and effective solution, edge computing offers greater flexibility and brings the data closer to the end user. This enables the creation of a faster, more reliable, and much more efficient computing solution.
Therefore, both edge computing and cloud computing complement each other in providing an effective response system that is foolproof and has no disruptions. Both computing methods work efficiently and in certain applications, edge computing fills and fixes the shortcomings of cloud computing with high latency, fast performance, data privacy, and geographical flexibility of operations.
Functions that are best managed by computing between the end-user devices and local networks are managed by the edge, while the data applications benefit from outsourcing data from everywhere and processing it through AI and ML algorithms. The system architects who have learned to use all these options together have the best advantage of the overall system of edge computing and cloud computing.
Learn more about different use cases on edge computing-
Condition-based monitoring - An Asset to equipment manufacturers (nife.io)