Edge VMs And Edge Containers | Edge Computing Platform
Edge VMs And Edge Containers are nothing but VMs and Containers used in Edge Locations, or are they different? This topic gives a brief insight into it.
Introduction
If you have just recently begun learning about virtualization techniques, you could be wondering what the distinctions between containers and VMs. The issue over virtual machines vs. containers is at the centre of a discussion over conventional IT architecture vs. modern DevOps approaches. Containers have emerged as a formidable presence in cloud-based programming, thus it's critical to know what they are and isn't. While containers and virtual machines have their own set of features, they are comparable in that they both increase IT productivity, application portability, and DevOps and the software design cycle (Zhang et al., 2018). The majority of businesses have adopted cloud computing, and it has shown to be a success, with significantly faster workload launches, simpler scalability and flexibility, and fewer hours invested on underlying traditional data centre equipment. Traditional cloud technology, on the other hand, isn't ideal in every case.
Microsoft Azure, Amazon AWS, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP) are all traditional cloud providers with data centres all around the world. Whereas each company's data centre count is continually growing, these data centres are not near enough to consumers when an app requires optimal speed and low lag (Li and Kanso, 2015). Edge computing is useful when speed is important or produced data has to be kept near to the consumers.
What is the benefit of Edge Computing?#
Edge computing is a collection of localized mini data centres that relieve the cloud of some of its responsibilities, acting as a form of "regional office" for local computing chores rather than transmitting them to a central data centre thousands of miles away. It's not meant to be a replacement for cloud services, but rather a supplement. Instead of sending sensitive data to a central data centre, edge computing enables you to analyse it at its origin (Khan et al., 2019). Minimal sensitive data is sent across devices and the cloud, which means greater security for both you and your users. Most IoT initiatives may also be completed at a lower cost by decreasing data transit and storage space using traditional techniques.
| The key advantages of edge computing are as follows: |
| - Data handling technology is better |
| - Lower connection costs and improved security |
| - Uninterruptible, dependable connection |
What are Edge VMs?#
Edge virtual machines (Edge VMs) are technological advancements of standard VM in which the storage and computation capabilities that support the VM are physically closer to the end-users. Each VM is a self-contained entity with its OS, capable of handling almost any program burden (Millhouse, 2018). The flexibility, adaptability, and optimum availability of such tasks are significantly improved by VM designs. Patching, upgrades, and care of the virtual machine's operating system are required regularly. Monitoring is essential for ensuring the virtual machine instances' and underpinning physical hardware infrastructure's stability. Backup and data recovery activities must also be considered. All of this adds up to a lot of time spent on repair and supervision.
| ### Benefits of Edge VMs are:- |
| - Apps have access to all OS resources. |
| - The functionality is well-known. |
| - Tools for efficient management. |
| - Security procedures and tools that are well-known. |
| - The capacity to run several OS systems on a single computer. |
| - When opposed to running distinct, physical computers, there are cost savings. |
What are Edge Containers?#
Edge containers are decentralized computing capabilities that are placed as near to the end customer as feasible in an attempt to decrease delay, conserve data, and improve the overall user experiences. A container is a sandboxed, isolated version of a component of a programme. Containers still enable flexibility and adaptability, although usually isn't for every container in an application framework, only for the one that needs expanding (Pahl and Lee, 2015). It's simple to reboot multiple copies of a container image and bandwidth allocation between them once you've constructed one.
| Benefits of Edge Containers are- |
| - IT management resources have been cut back. |
| - Spin ups that are faster. |
| - Because the actual computer is smaller, it can host more containers. |
| - Security upgrades have been streamlined and reduced. |
| - Workloads are transferred, migrated, and uploaded with less code. |
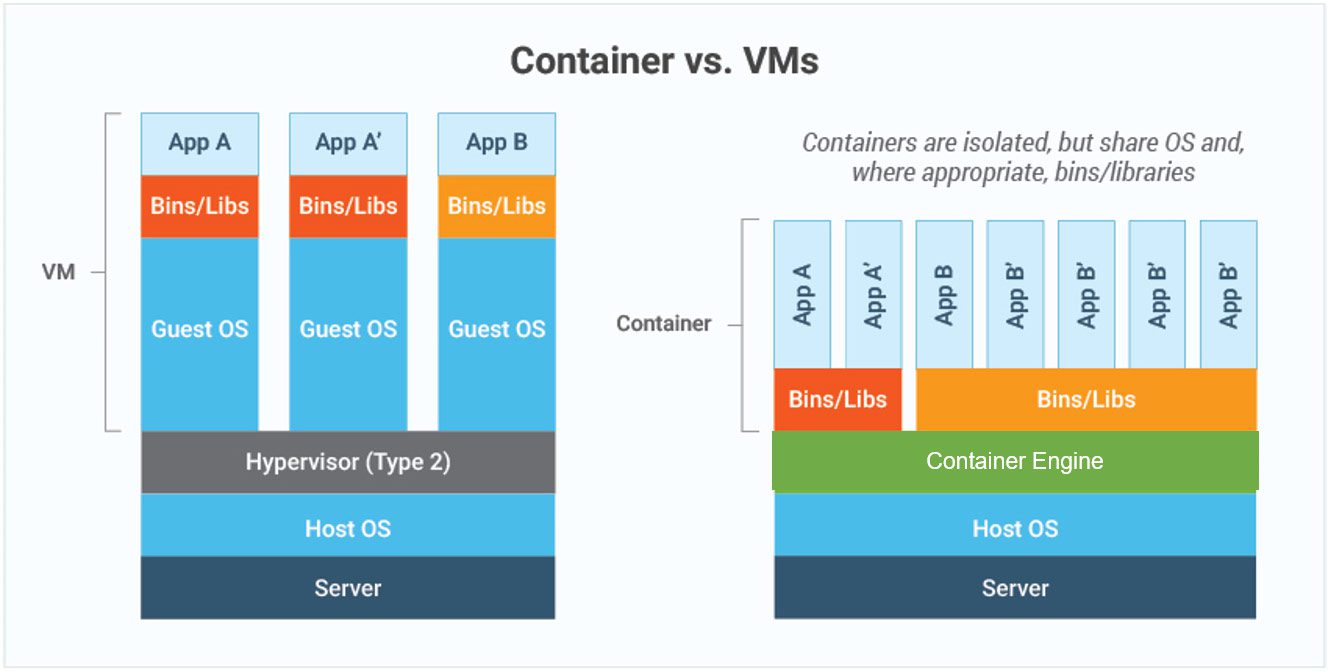
What's the difference Between VMs and Containers even without the context Edge?#
Containers are perfect where your programme supports a microservices design, which allows application programs to function and scale freely. Containers may operate anywhere as long as your public cloud or edge computing platform has a Docker engine (Sharma et al., 2016). Also, there is a reduction in operational and administrative costs. But when your application requires particular operating system integration that is not accessible in a container, VM is still suggested when you need access to the entire OS. VMs are required if you want or need additional control over the software architecture, or if you want or need to execute many apps on the same host.
Next Moves#
Edge computing is a viable solution for applications that require high performance and low latency communication. Gaming, broadcasting, and production are all common options. You may deliver streams of data from near to the user or retain data close to the source, which is more convenient than using open cloud data centres (Sonmez, Ozgovde and Ersoy, 2018). You can pick what is suitable for your needs now that you know more about edge computing, including the differences between edge VMs and edge containers.
Learn more about Edge Computing and its usage in different fields - Nife Blogs