Should you optimize your Docker container?
This blog explains the reasons for Docker container optimization and responds to the question "Should you optimize your Docker container?"

How Docker Works?#
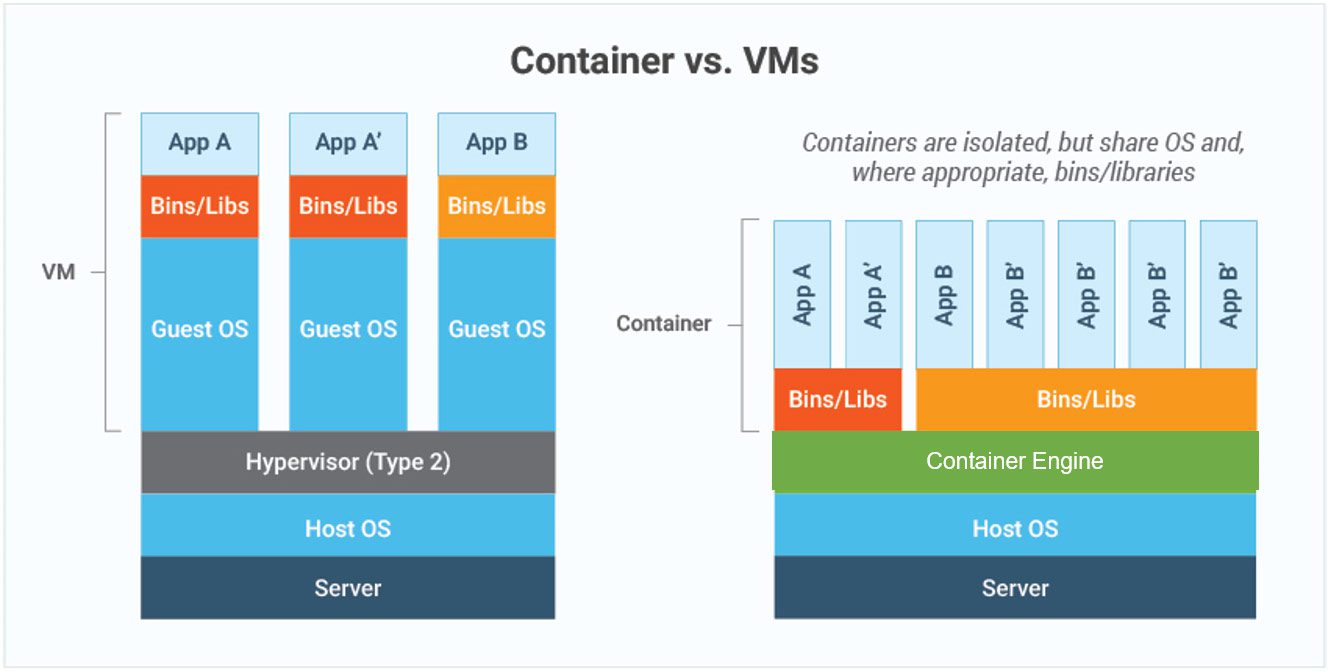
Docker is a leading containerization industry standard that aids in the packaging and distribution of programs in the most efficient manner feasible. Containers are a convenient approach to transporting software to various environments. They assist you in packaging your code with your desired environment settings and other platform-dependent parameters so that it may be quickly instantiated on other computers with little setup overhead [(Potdar et al., 2020)].
Simply put, Docker is an open-source solution that aids in the management of the containers we just covered. Docker, like containers, is platform-independent, as it supports both Windows and Linux-based platforms.
The Kubernetes vs. Docker debate#
When stated as a "both-and" issue, the distinction between Kubernetes and Docker becomes clearer. The truth is that you don't have to choose—Kubernetes and Docker are fundamentally different technologies that complement each other effectively for developing, deploying, and [scaling containerized applications].
Kubernetes and Docker collaborate. Docker is an open standard for containerizing and delivering software. Docker allows you to construct and execute containers as well as store and distribute container images. A Docker build can be simply executed on a Kubernetes cluster, but Kubernetes is not a comprehensive solution. Implement extra tools and services to handle security, governance, identity, and access, as well as continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) processes and other DevOps principles, to optimize Kubernetes in production [(Shah and Dubaria, 2019)].
Docker List Containers#
To list docker containers, use the commands 'docker container ls' or 'docker ps'. Both commands use the same flags since they both act on the same item, a container. It includes many parameters to achieve the result we want because it only shows operating containers by default. The command 'docker ps' is shorter and easier to type.
What Causes Docker Performance Issues?#
Docker is a sophisticated system that is affected by a variety of circumstances, including host settings and network quality. The following are some of the most prevalent causes of Docker slowness:
- Inadequate Resource Allocation
- Docker Image Sizes
- Size of Docker File Context
- Docker's default configuration is still in use.
- Latency in the network
How to Optimize Docker Containers?#
There are several ways to make Docker run quicker:
Appropriate Resource Allocation#
The host machine's performance has an impact on the container's performance. A sluggish CPU or inadequate RAM might create a bottleneck, causing Docker's performance to suffer [(Sureshkumar and Rajesh, 2017)].
Docker Image Optimization#
Examine the Dockerfile for the image and ensure that the file context is not too huge. The context contains a list of the files required by Docker to construct a container.
Examine the Dependencies#
Debian-based Docker images may create extra binaries and files while installing dependencies. Some of these interdependencies are not required for the container's usual operation and can be eliminated.
Consider Using Microservice Architecture#
Monolithic programs are typically slower than microservice-architected apps. If your Docker containers are struggling to operate, it might be because the app within the container is too large [(Wan et al., 2018)]. When the app is migrated to microservices, the workload may be distributed among several containers.
Make use of Dedicated Resources#
Hosting containers on the dedicated hardware of Bare Metal Cloud minimizes virtualization overhead and increases container performance. Containerized programs do not share system resources like RAM and CPU, which reduces latency and allows apps to fully exploit hardware.
Use a light operating system#
Building images using a lightweight system can save up to 100 MB of the final image size, resulting in much faster performance.
Dockerfile Layers Cache#
Layer caching can help you produce images faster. When Docker begins constructing an image, it searches the cache for layers with similar signatures and utilizes them [(Liu et al., 2018)]. This feature expedites the construction process.

Docker for Windows#
Docker containers initially only supported Linux operating systems. Docker may now operate natively on Windows, eliminating the requirement for Linux support. Instead, the Docker container will run on the Windows kernel itself, and the whole Docker tool set is now compatible with Windows. The Docker CLI (client), Docker compose, data volumes, and the other building pieces for Dockerized infrastructure are now Windows-compatible.
Conclusion#
Docker Container optimization is critical for overall performance. As more applications migrate to containerization, it is critical to maintaining them up to date on best practices. Otherwise, you risk losing some of the important advantages Docker has over traditional methods of software delivery, which would defeat the point of using Docker containers in the first place.