Five Essential Characteristics of Hybrid Cloud Computing
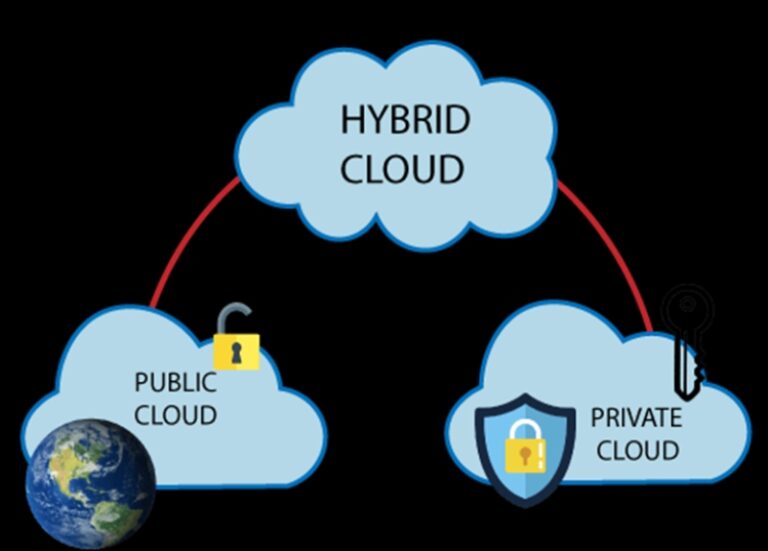
A hybrid cloud environment combines on-premises infrastructure, private cloud services, and a public cloud, with orchestration across multiple platforms. If you use a mixture of public clouds, on-premises computing, and private clouds in your data center, you have a hybrid cloud infrastructure.
We recognize the significance of hybrid cloud in cloud computing and its role in organizational development. In this blog article, we'll explore the top five characteristics that define powerful and practical hybrid cloud computing.

What is Hybrid Cloud Computing?#
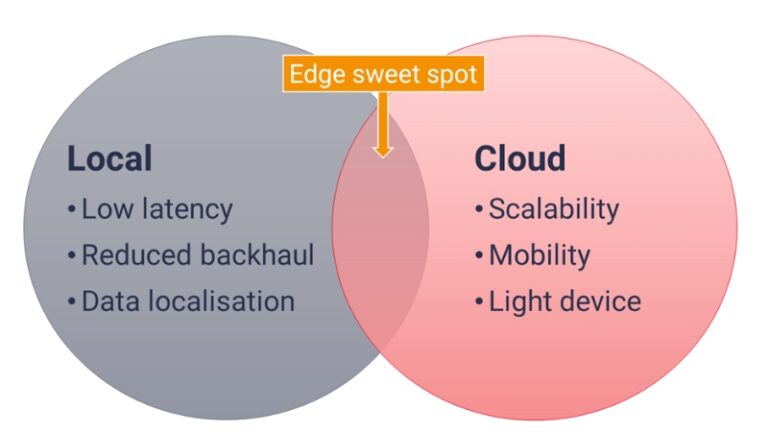
A hybrid cloud computing approach combines a private cloud (or on-premises data center) with one or more public cloud products connected by public or private networks [(Tariq, 2018)]. Consistent operations enable the public cloud to serve as an extension of a private or on-premises system, with equivalent management processes and tools. Because nearly no one nowadays relies solely on the public cloud, hybrid cloud computing options are becoming increasingly popular. Companies have invested millions of dollars and thousands of hours in on-premises infrastructure. Combining a public and private cloud environment, such as an on-premises data center and a public cloud computing environment, is a common example of hybrid cloud computing provided by AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud.
Hybrid Cloud Providers#
The digital revolution has radically changed the IT sector with the introduction of cloud computing. There are several hybrid cloud providers on the market, including:
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud
- VMware
- VMware Cloud on AWS, VMware Cloud on Dell EMC, HCI powered by VMware vSAN, and VMware vRealize cloud management
- Rackspace
- Red Hat OpenShift
- Hewlett Packard Enterprise
- Cisco HyperFlex solutions
- Nife Cloud Computing

Characteristics of Hybrid Cloud Computing#
Characteristic #1: Speed#
The capacity to automatically adjust to changes in demand is critical for innovation and competitiveness. The market expects updates immediately, and rivals are optimizing rapidly. Hybrid computing must be quick and portable, with maximum flexibility. Technologies like Docker and hybrid cloud providers such as IBM Bluemix facilitate this agility in a virtualized environment.
Characteristic #2: Cost Reduction#
One advantage of cloud computing is lowering expenses. Previously, purchasing IT assets meant paying for unused capacity, impacting the bottom line. Hybrid computing reduces IT costs while allowing enterprises to pay only for what they use. This optimization frees up funds for innovation and market introduction, potentially saving enterprises up to 30%.
Characteristic #3: Intelligent Capabilities and Automation#
Creating a digital experience in hybrid cloud computing requires integrating various technologies, which can be challenging for DevOps teams traditionally relying on numerous tools [(Aktas, 2018)]. Leveraging intelligent, unified, and centralized management capabilities enhances productivity and flexibility. IT automation in hybrid computing reduces human error, enforces policies, supports predictive maintenance, and fosters self-service habits.
Characteristic #4: Security#
Hybrid computing provides critical control over data and enhanced security by reducing data exposure. Organizations can decide where to store data based on compliance, regulatory, or security concerns. Hybrid architectures also support centralized security features like encryption, automation, access control, orchestration, and endpoint security, which are crucial for disaster recovery and data insurance [(Gordon, 2016)].
Characteristic #5: Lightweight Applications#
The final characteristic pertains to application size. DevOps teams need to develop agile apps that load quickly, boost efficiency, and occupy minimal space. Despite inexpensive storage, the focus should be on managing and understanding client data. Hybrid cloud computing supports DevOps in creating applications for global markets while meeting technological demands.

References#
Aktas, M.S. (2018). Hybrid cloud computing monitoring software architecture. Concurrency and Computation: Practice and Experience, 30(21), p.e4694. doi:10.1002/cpe.4694.
Diaby, T. and Rad, B.B. (2017). Cloud computing: a review of the concepts and deployment models. International Journal of Information Technology and Computer Science, 9(6), pp.50-58.
Gordon, A. (2016). The Hybrid Cloud Security Professional. IEEE Cloud Computing, 3(1), pp.82–86. doi:10.1109/mcc.2016.21.
Lee, I. (2019). An optimization approach to capacity evaluation and investment decision of hybrid cloud: a corporate customer's perspective. Journal of Cloud Computing, 8(1). doi:10.1186/s13677-019-0140-0.
Tariq, M.I. (2018). Analysis of the effectiveness of cloud control matrix for hybrid cloud computing. International Journal of Future Generation Communication and Networking, 11(4), pp.1-10.
Read more on Hybrid Cloud Computing: All You Need to Know About Hybrid Cloud Deployment